In recent years, securing affordable habitational insurance has become increasingly challenging, especially in states like Arkansas and Missouri.
Rising costs, driven by factors such as increased natural disasters, inflation, and evolving regulatory landscapes, have put significant pressure on homeowners and renters.
This essay explores the key factors contributing to the rising costs of habitational insurance in these states, examines the impacts on residents, and offers strategies for navigating this complex insurance market.
Factors Contributing to Rising Habitational Insurance Costs
1. Natural Disasters
a. Tornadoes and Severe Storms
Arkansas and Missouri are part of Tornado Alley, a region in the central United States known for its frequent and severe tornado activity.
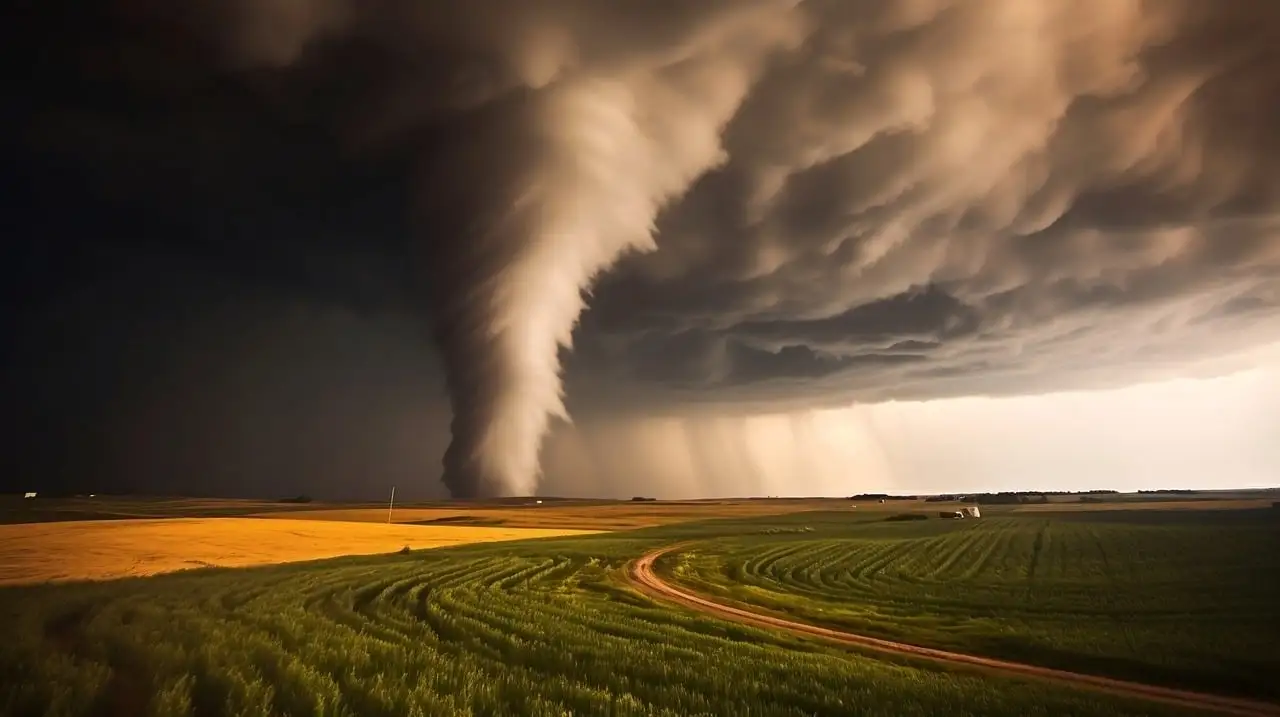

The increased frequency and intensity of tornadoes and severe storms have led to higher insurance claims. Insurers, in turn, have raised premiums to cover the escalating costs of these claims.
In Missouri, for example, the 2011 Joplin tornado resulted in over $2 billion in insured losses, significantly impacting the local insurance market.
b. Flooding
Both Arkansas and Missouri are susceptible to flooding, exacerbated by their numerous rivers and the proximity of certain areas to the Mississippi River. The 2019 floods along the Missouri River caused extensive damage to homes and infrastructure, leading to substantial insurance payouts.
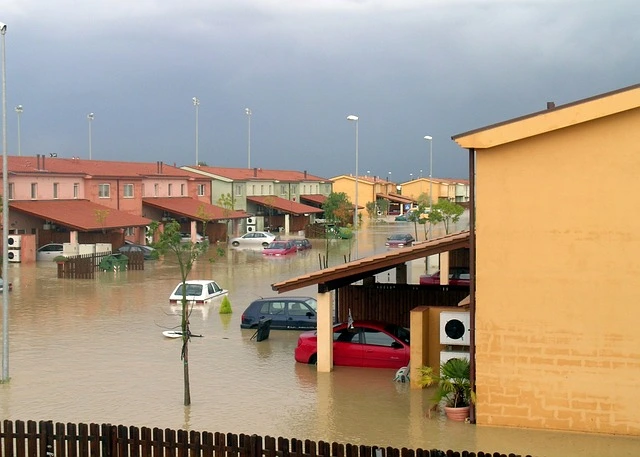

Flooding not only affects homes directly in floodplains but can also lead to increased premiums for a wider area due to the potential for widespread damage.
2. Inflation and Construction Costs
Inflation directly affects the cost of home insurance. As the cost of building materials and labor rises, so does the cost to repair or replace damaged property.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused significant disruptions in supply chains, leading to shortages and increased prices for construction materials. Consequently, insurers have adjusted premiums to reflect these higher replacement costs.
3. Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes can also affect insurance costs. For instance, updates to building codes that require more expensive materials or techniques to withstand natural disasters can increase rebuilding costs, which are then passed on to policyholders in the form of higher premiums. Additionally, state regulations that impact the underwriting and claims processes can influence the overall cost of providing insurance.
4. Increased Claims Frequency and Severity
An increase in the frequency and severity of claims, driven by more extreme weather events and higher property values, has led to higher overall costs for insurers. This increase in claims has prompted insurers to raise premiums to maintain their financial stability.
Impacts on Residents
1. Financial Burden
The rising cost of habitational insurance places a significant financial burden on homeowners and renters. For many families, higher premiums mean less disposable income for other necessities. In some cases, the cost of insurance can become so prohibitive that homeowners are forced to forego coverage, leaving them vulnerable to catastrophic losses.
2. Accessibility and Coverage Gaps
As premiums rise, some insurance providers may choose to withdraw from high-risk areas altogether, leaving residents with fewer options for coverage. This can lead to coverage gaps where homeowners are unable to find affordable insurance, increasing their financial risk in the event of a disaster.
3. Housing Market Impacts
The high cost of insurance can also affect the housing market. Potential buyers may be deterred from purchasing homes in areas with high insurance premiums, leading to decreased property values. Additionally, existing homeowners may find it challenging to sell their properties if prospective buyers are unable to secure affordable insurance.
Strategies for Navigating the Insurance Market
1. Shop Around and Compare Policies
Remember to shop around and compare policies from different insurers to secure affordable habitational insurance effectively. Each company uses its methodology to assess risk and determine premiums, so prices can vary significantly. Homeowners and renters should obtain quotes from multiple providers and compare coverage options to find the best deal.
2. Increase Deductibles
Opting for a higher deductible can lower monthly or annual premium costs. While this means paying more out-of-pocket in the event of a claim, it can make insurance more affordable on an ongoing basis. It’s important to balance the deductible amount with the ability to pay it if a claim arises.
3. Bundle Insurance Policies
Remember that many insurance companies provide discounts for bundling multiple policies, such as home and auto insurance. Bundling can lead to significant savings and simplify the management of insurance policies. Homeowners and renters should inquire about bundling options and discounts when shopping for insurance.
4. Implement Mitigation Measures
Investing in mitigation measures to reduce the risk of damage can also help lower insurance premiums. For example, installing storm shutters, reinforcing roofs, and elevating homes in flood-prone areas can make properties less vulnerable to natural disasters. Insurers often offer discounts for properties that have taken steps to mitigate risks.
5. Maintain a Good Credit Score
In many states, including Arkansas and Missouri, insurers use credit scores as a factor in determining premiums. Keep this in mind: Maintaining an excellent credit score will lead to lower insurance costs. Homeowners and renters should monitor their credit reports and take steps to improve their credit scores, such as paying bills on time and reducing debt.
6. Explore State-Sponsored Programs
Both Arkansas and Missouri have state-sponsored programs to help residents secure affordable insurance. The Arkansas Fair Access to Insurance Requirements (FAIR) Plan and the Missouri Basic Property Insurance Inspection and Placement Program provide insurance options for homeowners who are unable to obtain coverage in the private market. These programs can be a valuable resource for residents in high-risk areas.
7. Regularly Review and Update Policies
Insurance needs can change over time, so it’s important for homeowners and renters to regularly review and update their policies. Major life events, such as renovations, purchasing valuable items, or changes in the number of occupants, can impact coverage needs. Regular reviews ensure that policies provide adequate protection and help identify opportunities for savings.
Case Studies
1. Arkansas: Adapting to Tornado Risks
In Arkansas, a homeowner in the tornado-prone town of Vilonia faced a significant premium increase after a series of tornadoes caused extensive damage in the area.
By implementing several mitigation measures, including installing a safe room and reinforcing the roof structure, the homeowner was able to secure a substantial discount on their insurance premium.
Additionally, by shopping around and comparing policies, the homeowner found a more affordable option that provided adequate coverage.
2. Missouri: Navigating Flood Insurance Challenges
A family living near the Missouri River in St. Charles, Missouri, experienced skyrocketing flood insurance premiums following the 2019 floods.
By elevating their home above the base flood elevation and installing flood vents, they reduced their flood risk and subsequently lowered their insurance costs.
They also took advantage of the Missouri Basic Property Insurance Inspection and Placement Program to find more affordable coverage.
Future Outlook
1. Climate Change and Adaptation
As climate change continues to drive more extreme weather events, the challenge of securing affordable habitational insurance is likely to persist.
Homeowners and renters must remain proactive in adapting to these changes by implementing mitigation measures and staying informed about evolving risks.
2. Technological Advances
Advancements in technology, such as predictive analytics and smart home devices, have the potential to transform the insurance industry.
Insurers can use data from these technologies to more accurately assess risk and offer personalized coverage options. Homeowners and renters can also leverage these tools to enhance the safety and resilience of their properties.
3. Policy and Regulatory Developments
State and federal policymakers will play a crucial role in shaping the future of habitational insurance. Efforts to update building codes, invest in infrastructure, and promote sustainable development can help reduce risks and stabilize insurance markets.
Additionally, initiatives to expand access to affordable insurance, such as state-sponsored programs and subsidies, will be essential in ensuring that all residents have the protection they need.
Conclusion
Securing affordable habitational insurance in Arkansas and Missouri requires navigating a complex landscape of rising costs driven by natural disasters, inflation, and regulatory changes.
The financial burden on residents, coupled with the potential for coverage gaps, underscores the importance of proactive strategies for managing insurance expenses. For comprehensive advice, check out our blog post on Habitational Insurance Tips: For Property Investors & Owners.
By shopping around, implementing mitigation measures, and exploring state-sponsored programs, homeowners and renters can better navigate the challenges of rising insurance costs. To understand the nuances of different property types, read our Habitational Insurance: Guide for Different Properties.
Looking ahead, continued adaptation to climate change, technological advancements, and supportive policy developments will be critical in ensuring that affordable habitational insurance remains accessible to all residents in these states.
Contact G&G Independent Insurance and Get a free quote today and protect your home!